a. Superior frontal gyrus
b. Inferior frontal gyrus
c. Cingulate sulcus
d. Insula
b. Inferior frontal gyrus
c. Cingulate sulcus
d. Insula
A comprehensive question bank for indian medical PG preparations- AIIMS, ALL INDIA, JIPMER, PGI, state exams etc. Visual and audio content prepared in view of upcoming pattern of NEET (National Eligibility & Entrance Test). Best wishes for your preparation! AIPGE content updated with emphasis on recent questions.


| Superior medullary velum | |
|---|---|
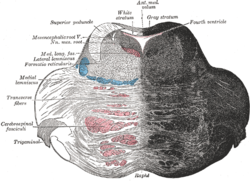
Coronal section of the pons, at its upper part. (Ant. med. velum labeled at center top.)
| |

Anterior view of the cerebellum. (Ant. medullary velum labeled at center top.)
| |
 |
| "Brainstem trochlear". Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikipedia - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Brainstem_trochlear.png#/media/File:Brainstem_trochlear.png |